Choosing the Right System Memory (DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5) for PC or Mac
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a type of computer memory that can be accessed randomly, meaning any byte of memory can be accessed without touching the preceding bytes. RAM is volatile memory, which means it is wiped clean when the power is turned off.
There are two main types of RAM: dynamic RAM (DRAM) and static RAM (SRAM). DRAM stores each bit of data in a separate capacitor within an integrated circuit, and must be constantly refreshed or it will lose its data. SRAM uses flip-flops to store each bit of data, and does not need to be refreshed like DRAM. SRAM is faster and more expensive than DRAM, but also requires more power and is less dense, meaning it requires more space on a chip.
When a computer is turned on, the operating system and other programs are loaded from the hard drive into RAM. The processor then retrieves instructions and data from RAM as needed to perform tasks. When a program or data is no longer needed, it can be removed from RAM to make room for other programs and data.
RAM is an important component of a computer system, as it determines how quickly a computer can access and process data. More RAM can help a computer run faster and more efficiently, but it also increases the cost of the system.
Memory Latency
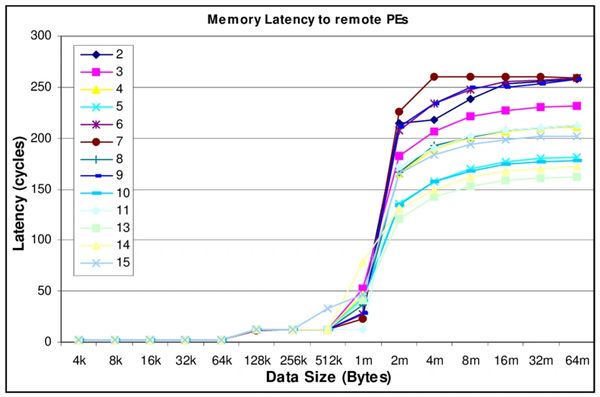
Memory latency refers to the time it takes for a computer's central processing unit (CPU) to access data from its main memory. This can be affected by a number of factors, including the speed of the memory itself and the architecture of the system.
There are several types of memory that a computer can use, including RAM (random access memory) and ROM (read-only memory). RAM is used for storing data that the CPU needs to access quickly, while ROM is used for storing data that does not need to be changed, such as the system's BIOS (basic input/output system).
The CPU retrieves data from memory by sending a request to the memory controller, which manages the flow of data between the CPU and the memory. The memory controller accesses the requested data and sends it back to the CPU, which can then use it to perform the necessary operations.
The time it takes for the CPU to access data from memory is known as the memory latency. This is typically measured in nanoseconds (ns) or clock cycles. A lower memory latency means that the CPU can access data from memory more quickly, which can improve the overall performance of the system.
Memory technologies (such as DDR3, DDR4, DDR5)
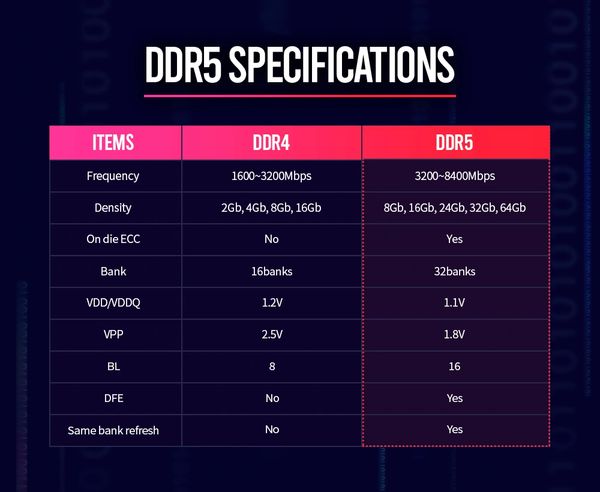
DDR3 (double data rate 3) is a type of dynamic random access memory (DRAM) that is commonly used in computers. It is an improvement over previous versions of DDR memory, with faster data transfer rates and lower power consumption. DDR3 memory operates at a higher frequency than DDR2 memory and is capable of transferring data at speeds of up to 2133 megatransfers per second (MT/s).
DDR4 (double data rate 4) is a newer type of DRAM that is even faster and more efficient than DDR3. It can transfer data at speeds of up to 3200 MT/s and has a lower power consumption compared to DDR3. DDR4 is commonly used in modern computers and is the successor to DDR3.
DDR5 (double data rate 5) is the latest generation of DDR memory. It is even faster than DDR4, with data transfer rates of up to 6400 MT/s. DDR5 also has a lower power consumption than DDR4 and includes additional features to improve reliability and performance. DDR5 is beginning to be used in some high-end computers and servers.
All of these memory technologies are used to store data that the CPU can access quickly. By using faster memory technologies, a computer's performance can be improved, as the CPU can access data from memory more quickly.
Memory Bandwidth
Memory bandwidth is the amount of data that can be transferred to and from the computer's main memory in a given amount of time. It is typically measured in megabytes per second (MB/s) or gigabytes per second (GB/s). Memory bandwidth is an important factor in determining the overall performance of a computer, as it determines how quickly the CPU can access data from memory.
There are several factors that can affect memory bandwidth, including the type of memory being used, the speed of the memory, and the architecture of the system. For example, a computer with faster memory and a larger memory bus (the connection between the CPU and the memory) will generally have a higher memory bandwidth than a computer with slower memory and a smaller memory bus.
Improving memory bandwidth can be an effective way to increase the overall performance of a computer. This can be achieved by using faster memory, increasing the size of the memory bus, or using memory technologies that are more efficient at transferring data.
Error-correcting code (ECC) Memory
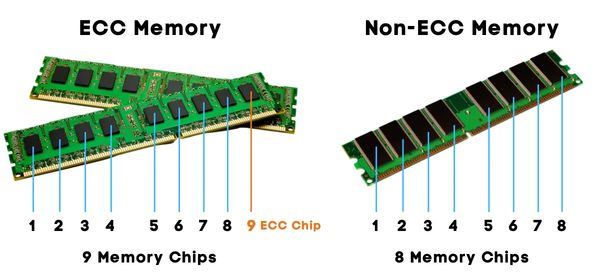
Error-correcting code (ECC) memory is a type of computer memory that is designed to detect and correct errors in the data stored in memory. It does this by adding extra bits to the data stored in memory, which can be used to detect and correct errors when the data is read back from memory.
ECC memory is typically used in servers, workstations, and other systems where data integrity is important. It is more expensive than non-ECC memory, but it provides a higher level of reliability, as it can detect and correct errors that may otherwise go unnoticed.
ECC memory works by using an algorithm to calculate a checksum for the data stored in memory. The checksum is a value that is derived from the data and is used to verify the integrity of the data. When the data is read back from memory, the checksum is recalculated and compared to the original checksum. If the two values do not match, it indicates that an error has occurred, and the ECC memory can correct the error using the extra bits that were added to the data.
ECC memory is typically used in systems that require high levels of reliability, such as servers and workstations. It can help to prevent data corruption and ensure that data is accurate and reliable.
Stay Informed About the Latest Computer Hardware Deals!
Sign up for our mailing list to receive updates on new products, discounted laptops and computer parts, and exclusive sales and discounts. Stay up-to-date on the latest hardware trends and tips with our newsletters. Don't miss out on the best deals – join our mailing list today!
Located in Downtown DeLand since 2003, Offering Fast Friendly service at an affordable price! We service Any Brand PC or Mac! Central Florida Computer Dealer, Wholesalers Welcome!
Copyright © 2020 Wholesale Computer Outlet, LLC D - All Rights Reserved. Check out our Reviews!
106 North Woodland Blvd DeLand, Florida 32720
Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies. By continuing to use this site, you accept our use of cookies.